Firstly let us start with an example, you have a Laptop/PC which is configured with some hardware components like RAM, Hard-disk, and CPU, on top of it you have Operating System (most likely Windows), and above that you have software. On software, you can have your applications.
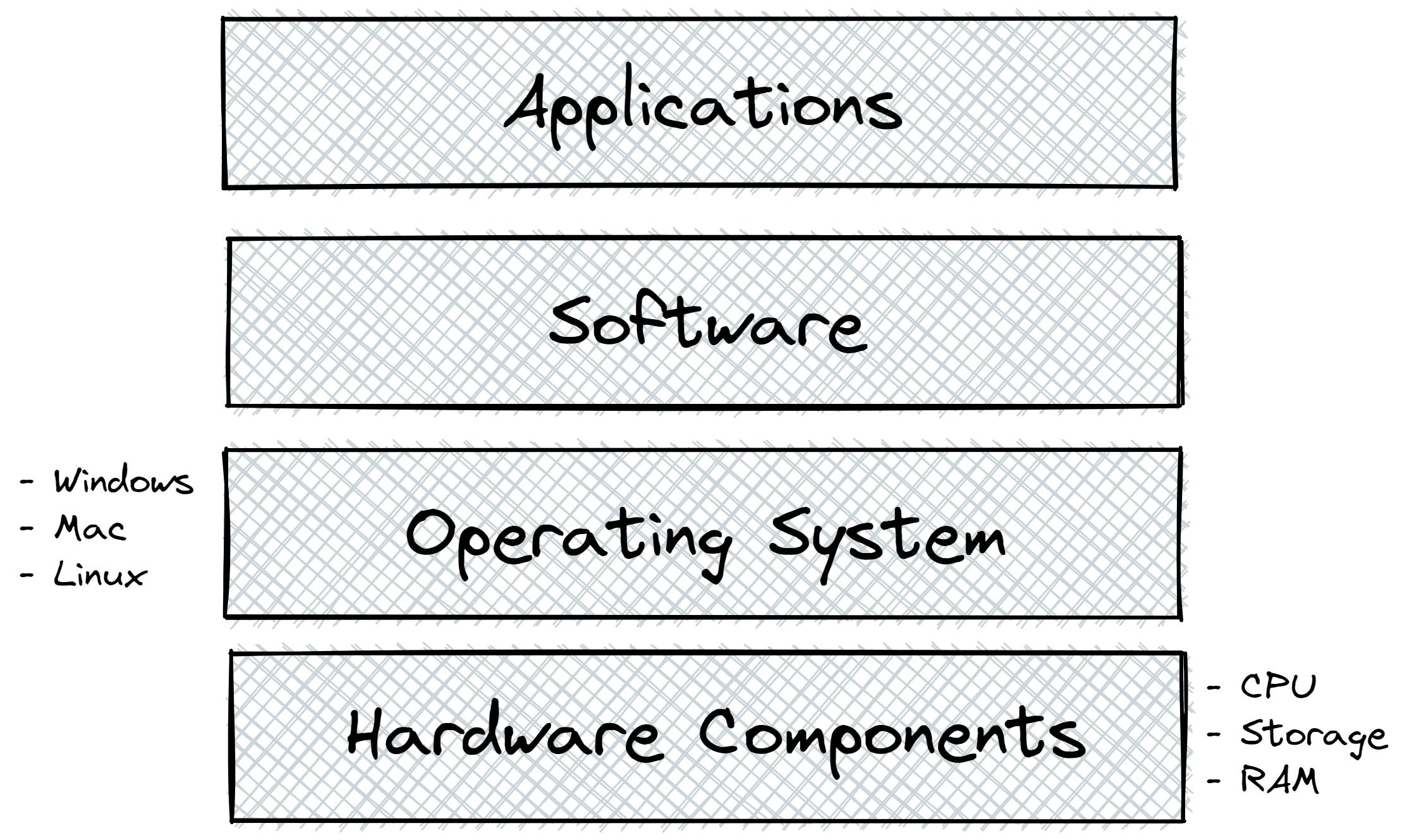
This is just the sample architecture of any machine.
Now you are using your machine as per your need.
Suppose there may be a situation where you must have another OS like Linux or Mac, What do you need to do now?
You have to buy other machines that have Linux or Mac OS and use them for that need.
This seems silly when you have a small work with that OS but you need to buy the entire machine for that use case.
Then what is the solution for similar kinds of situations?
Here is where Virtualization came into the picture.
Virtualization means, creating a virtual machine on top of an existing machine by using the hardware components assigned to that existing component.
With the previous example, we suffered from a problem of wanting to need another OS for small use, with virtualization we can create a virtual machine of Linux OS say on top of an existing machine of Windows OS.
Yeah, it's fine we can use one OS on top of another OS. But, how can we do that?
We can do this with software called Hypervisor. It is software that creates and runs virtual machines.
As we have seen in the basic architecture of a machine above, we have some software on top of the OS, here where Hypervisor stays and takes control as required.
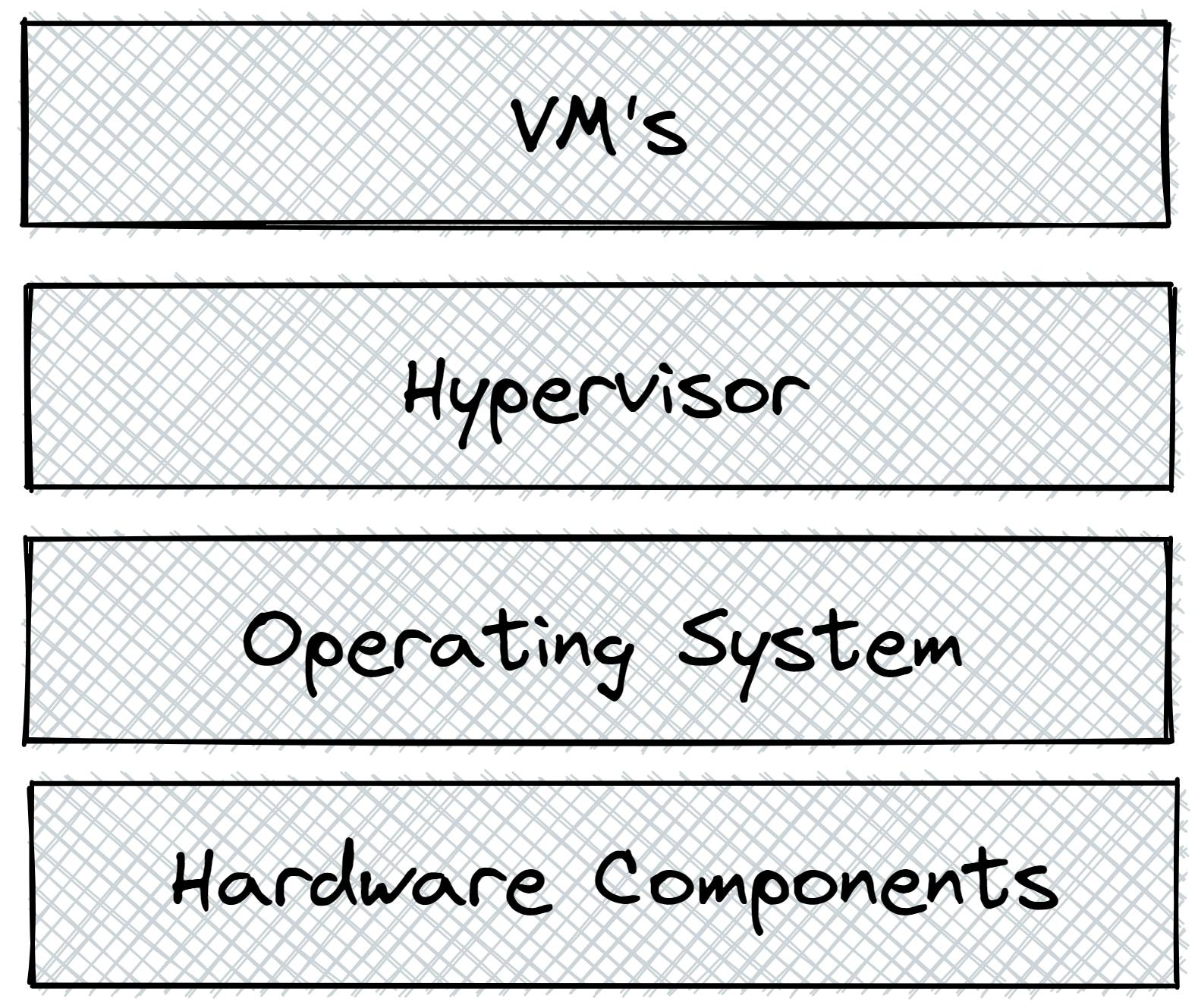
This means we can have n number of VMs with a single set of Hardware components.
Benefits of Virtual Machines
Learn and Experiment: let us assume you have Mac OS, but you want to experience the Linux OS at that particular time you can install a hypervisor on your OS and download Linux OS on top of Mac OS
You need not have to buy a new computer for that
Your main OS is safe if there are misconfigurations in that OS, No danger to the main OS since it is isolated
Test your app on different OS: If you are a developer you want to see how your application is working with other systems/OS, at that particular time you can install multiple OS on top of your main OS for testing your application.
We have come across Hypervisors, right?
If we go in-depth, we have two types of hypervisors.
Type 1 or bare-metal hypervisor.
Type 2 or hosted hypervisor.
Type 1 Hypervisor
These were the hypervisors that create the VMs on top of the bare metals.
That means there is no intermediate operating system between hardware components and the hypervisor.
Microsoft Hyper-V and VMware vSquare are examples of type 1 hypervisors.
Type 2 Hypervisor
These were the hypervisors that create the VMs on top of the existing OS.
As we observed in the previous examples we installed a hypervisor on top of a specific OS, those were the type 2 hypervisors.
VMware Workstation and Oracle VirtualBox are examples of type 2 hypervisors.
Many cloud providers use this virtualization i.e, hypervisors.
How?🤔
What cloud providers do is, install a large data center at some place where they will have many physical servers installed, on top of physical servers they install type 1 hypervisor.
Whenever you require a particular instance they request the hypervisor of any server in that data center and that creates a VM of supplied configurations. Hence our instance gets created. This is how they use virtualization.
These are just the basics of virtualization, there will be a more in-depth concept with containers and some other stuff which we look into it later.

